An ear infection is not contagious as it is caused by environmental factors such as viruses, bacteria, and allergens and not by direct contact with an infected person. Nevertheless, the cause of illness can spread from one person to another.
Younger children and infants are more vulnerable to experiencing an ear infection as they are more likely to suffer from clogged tubes, which are comparatively narrower, less rigid, and shorter than adults.
Can an ear infection be contagious is one question that most parents wonder about when sending their kids off to school. You might have worried it's widespread, particularly in younger children, typically affecting the middle ear. It occurs due to bacterial or viral infections causing ear pain.
However, adults can get them too, and you have undoubtedly experienced one at some point in your life. But the main question which arises is, are ear infections contagious?
This blog looks into contagious ear infections to help you understand the right diagnosis and treatment options.
Ear Infection- An Overview
An ear infection, otitis media, is a condition that often results from a viral and bacterial infection that affects the middle ear. One of the most common symptoms associated with an ear infection is ear pain [1, 2].
An ear infection is usually painful and may also trigger signs of tinnitus. You start hearing sounds that aren’t there. Hearing your heartbeat or breathing echoing in your ear or your ear being increasingly itchy can be another sign that your ear is infected.
There are several different ear infections, where some are more significant than others. Such ear infections may or may not be contagious. Though the condition cannot spread from person to person, the cause of the illness certainly can.
How Common Is Otitis Media In Children?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that about 30 million people suffer from otitis media (OM) every year. This suggests that half of all American children will experience an ear infection at some point in their lives.
About 90% of children between 6 months to 5 tears of age suffer from ear infections each year [3].
Types Of Otitis Media
There are three types of ear infections:
External ear infection
This kind of infection is known as a swimmer’s ear. Swimmer’s ear, also known as otitis externa, is an infection of the outer ear and is one of the other types of ear infections.
Bacteria and fungus grow in the ear canal as a result of moisture. Numerous skin diseases, including eczema and acne, can cause it to flare up. In these situations, scratches occur on the skin of the ear canal.
It can cause anything from pain to itchiness or swelling, and you may also notice a discharge. Such infections usually clear up in ten days.
Swimmers whose ear aches frequently last longer than expected should take antibiotics. For instance, drops or ointment can remove fungus or bacteria that may be present in the ear.
The use of over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen can also be effective. Keeping the ear as dry as possible is advisable, so be careful while bathing and avoid swimming.
Such signs of infection are more prevalent during vacations. Children diving underwater or spending time at a water park increases the disease risk.
Inner ear infection
An inner ear infection is when the inner ear gets inflammation due to a virus and bacterial infection. It affects the parts of the ear responsible for balance and hearing called labyrinthitis.
Viral infection is the leading cause of inner ear infections. When your inner ear gets infected, you may feel dizzy, nauseous, vomiting, earache, spinning sensation, hearing loss, etc.
Middle ear infection
The most common form of ear infection most children suffer from is otitis media. Otitis media or middle ear infection is the main problem that most experience.
It often starts with an infection that impacts the throat or the nose before moving to the ear. So, symptoms can be similar to getting a cold or having the flu.
Once the infection starts, it can spread to different areas, such as the Eustachian pipes. The formation of mucus blocks the pipes. It prevents things from draining due to bacteria development. The mucus is red or cloudy in case of infection.
What Causes Ear Infection?
Ear infections develop from viruses and bacteria spread in the middle ear. It is more common in people with nasal congestion and when they have swelling in the eustachian tubes. These are responsible for regulating air and draining fluid in the ear.
Any form of inflammation and swelling in the eustachian tubes can cause blockage resulting in the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. It often causes ear pain, pressure, and headaches.
Some other factors that may block your eustachian tubes, causing an ear infection include-
changes in air pressure
-
Swollen Adenoids.
-
Seasonal Changes.
-
Allergies.
-
Smoking.
-
Sinus Infections.
When Should A Parent Suspect An Ear Infection?
As cases of ear infections are more prevalent in children, parents should always stay alert. Acute otitis media, the medical term for common ear infection, should be suspected by parents when a child is suffering from ear pain, irritability, or fever.
Many children with ear infections suffer from colds as the first sign of the condition.
Signs To Watch Out For In Children
Children between six and eighteen months are at a higher risk of ear infections. If your child is commonly experiencing ear infections around this age, it can lead to developmental to language delays.
As such, you must ensure that you are watching out for the signs of an issue here. If ear infections occur regularly in a child of this age, you must take them to see a doctor so they can get appropriate treatment.
One of the issues is that children during this age are often non-verbal. You might know they are in pain due to their actions or emotions. However, you won’t be able to pinpoint the cause of their pain, and they won’t be able to tell you.
What Are Common Ear Infection Symptoms?
The symptoms of ear infections show very rapidly. But the good thing is that ear infections go away without requiring major medical attention. Some of the symptoms of ear infections include:
-
Ear pain
-
Irritability
-
Itching
-
Fluid coming out from the ear
-
Balance problem (in case of a young child)
-
Fever
-
Sore throat
-
Hearing problem
-
Fussiness
-
Headache
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed?
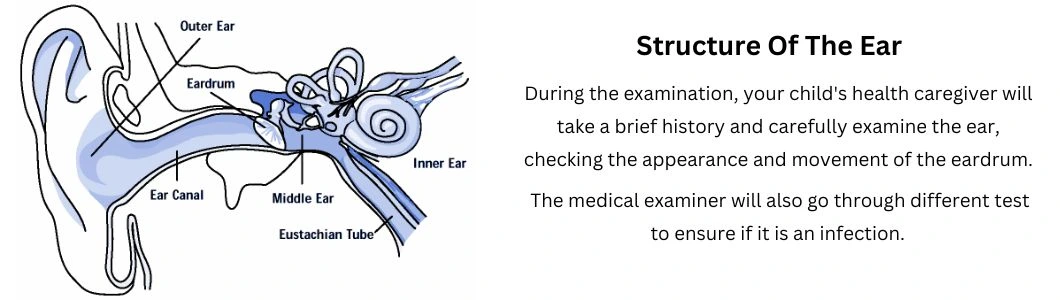
An ear infection can be diagnosed by proper medical examination. It is best to consult a doctor within 24 hours of noticing the symptoms.
A physician will use an instrument called an otoscope to look into the ear. The Pneumatic otoscope is an instrument that helps doctors to look into the ear to check the presence of fluid behind the eardrum. Using this instrument, the doctor gently puffs air against the eardrum. In normal cases, the ear drum will move; however, in cases where it is filled with fluid, there will be little to no movement of the eardrum [4].
They may also use a stethoscope to listen to your child's breathing.
Additional tests done to diagnose ear infection includes the following.
-
Tympanometry- It helps in measuring the movement of the eardrum. It works by sealing off the ear canal and adjusting the air pressure that causes the eardrum to move.
-
Tympanocentesis- This diagnosis method is not frequently used. It is done by causing a tiny pierce in the eardrum to drain the fluid from the middle ear. Then this fluid is tested for the presence of bacteria and viruses.
-
Acoustic reflectometry- It is a test that is done to check how much sound is reflected back from the eardrum. It is an indirect measure of fluids in the middle ear.
Are Ear Infections Contagious?
In most cases, an ear infection is not contagious. Though the condition cannot spread from person to person, the cause of the illness certainly can. People who share a bed or stay together are more prone to spread the disease.
In simple words, one can catch the virus that may cause an ear infection from someone else suffering from the same condition.
Such viruses spread through the air via sneezing and coughing of an infected person. One can also get infected by touching the surfaces where the droplets containing the virus have landed.
The bacteria causing ear infections are normally present in the respiratory tract, but they cause infection only in conditions such as having a blocked eustachian tube.
Are Outer Ear Infection Contagious?
No, outer ear infections are not contagious, but the virus and bacteria may pass from one person to another through droplets. Confused?
These viruses may travel from one person to another through saliva, but they do not necessarily cause an ear infection in the other person. It may also result in a cold.
To break it down further-
-
Inner ear infection is not contagious and often go away with time without any medication.
-
Out ear infection may occur from swimming and is also not contagious. However, it may require an antibiotic eardrop treatment.
How Is An Ear Infection Treated?
The good news is that these infections will often disappear within three days or two weeks. You won’t usually be prescribed medicines unless the issue persists.
The first few treatment options for ear infections include-
-
Antibiotics like ear drops for a severe infection.
-
Warm compresses
-
Medications like ibuprofen.
You might get a middle ear infection more often if you have an issue with your immune system or are around tobacco smoke. It’s common for people who spend time around crowds to develop infections.
Are These Infections Dangerous?
A swimmer’s ear is not considered to be dangerous. However, they can have painful repercussions. It’s common for ears to ‘pop’ on a plane due to the high high-pressure level. Ear infection causes more pressure, thus resulting in severe pain and loss of hearing.
Aside from this, the infection may spread, and children could experience repeated infections. Generally speaking, more serious issues will occur when there is an underlying medical condition.
For instance, if you or your child has a weakened immune system, then ear infections can and perhaps should be more of a concern. At the very least, you will need to keep an eye on them and take more care to ensure they do not spread.
Middle ear infections are not severe but can occur on rare occasions. For instance, the infection can spread to the inner area or the brain’s lining leading to meningitis. Temporary hearing loss is also possible, that is, vertigo which causes the individual to feel dizzy and potentially nauseous.
Why Are Ear Infections Common In Children?

People may wonder why ear infections are more common in children. Among several reasons, the leading cause is their eustachian tubes, which get clogged with mucus, and are shorter. The horizontal angle also means the connection is far more likely to get infected and clogged.
There are other factors to consider too. For instance, a child born prematurely with Down syndrome or a Cleft palate could be more likely to develop this issue. A pacifier may also be an issue, mainly if you do not keep it clean, as this will spread bacteria. Another reason is that children often lie back while feeding or drinking.
So, how many ear infection symptoms in children are too many? Typically, if a child is experiencing three infections each six months or four conditions within a year, this should be a cause for concern. It is when long-term effects can become an issue and why you must make sure that you visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Can Ear Infections Be Prevented?
There are many ways that can help people in preventing an ear infection, some of which are listed below.
Use earplugs to avoid loud noise
Nearly 15% of Americans experience hearing loss due to noisy work or recreational environments. Thus you can reduce harmful sound levels and maintain the original sound quality as closely as possible.
Turn the volume down
To save your ear, you should avoid the risk of noise-induced hearing loss due to the unsafe use of audio devices. To do that, when you enjoy music through headphones and earbuds, don’t raise the volume by more than 60, and don’t use headphones for more than 1 hour at a stretch.
Give Time To Ear For Recovery
When you are in an environment exposed to loud noise for a prolonged period, like in a bar or a concert, your ears need time to recover. If there is a provision, every five minutes, step outside and let your ears take some rest. According to the researchers, our ears need approximately 16 hours to recover from one night of loud sound.
Using Cotton Swabs Can Be Dangerous
Cotton swabs to clean wax out of the ear canal is unsafe, as inserting anything in the ear canal can damage the eardrums. To clean excess wax, you can use a damp towel. You also take the help of an ENT specialist.
Get Up And Move Your Body
Like other parts of our body, exercise is good for our ears. When we exercise, it can regulate blood flow to all aspects of our body, including the ears. Thus, it helps the ears’ internal parts stay healthy and work with maximum potential.
Manage Your Stress And Anxiety Level
Tinnitus, a fictitious ringing in the ear is connected to temporary and permanent stress and anxiety. So it is important to manage the stress and anxiety symptoms.
The use of Nootropics can reduce the symptoms of stress and anxiety. Waklert 150 mg is an effective Nootropic that the FDA approved to manage the signs of stress. It takes 30 minutes to start acting, and its action can last 12 to 14 hours. However, the use of Waklert 150 mg should be done under the supervision of a doctor.
Avoiding The Spread Of Swimmer’s Ear
If you are keen to avoid this possibility, you or your child should ensure that you wear waterproof earbuds. These will keep the water and moisture out of your ear completely. These earbuds adapt and can be molded to the specific shape of your ear to ensure that there is absolutely no way that any water can escape.
However, sound can still travel in and out, so you can still hear, which means they are safe for public use. You can also wear them for a music concert as they work as protection.
Other causes and issues that may result in swimmers’ ears would be using earphones or earbuds and using anything to clean out your ears that should not be there.
You shouldn’t insert anything inside your ear if you think it is dirty. It can be dangerous and potentially cause an infection to spread. Always seek professional advice if you have concerns about ear wax buildup in your or your child’s inner ear. They will be able to provide the correct type of clean-out that won’t cause a risk of infection.
You can clean parts of the ear yourself, but this should only be the absolute outer ear. Try with a damp cloth. When you tend your outer ear, ensure that you are using a clean towel and that any earbuds or anything near the ear are also clean. Avoid using other towels in a water park or swimming pool. It will cause an infection to spread.
Avoiding The Spread Of A Middle Ear Infection

If you want to ensure you avoid this type of common infection, then there are some steps you can take.
-
Get a flu shot regularly
-
Make sure to clean the visible part of the ear.
-
Refrain from putting foreign objects inside your ear
-
Ensure that you wash your hands regularly.
Is follow-up care necessary?
If the signs improve within the next 24 hours after taking the medication or even without any medical attention, the doctor may not call for a visit for the next 2 to 4 weeks. However, in cases where the symptoms do not resolve in the next 48 hours, the child is often re-examined.
Is Ear Infection Contagious- A Word From Healthmatter
Ear infections are not serious by themselves, but they can have severe complications and cause issues. It’s best to take adequate measures we have mentioned to avoid them where possible.
It will be possible if you keep the ear clean, do not insert any foreign objects inside the ear, practice good hygiene and be careful about public items you are using.
If the symptoms of infection become severe, it is advisable to seek medical help. It is a concern for most children and people with weak immune systems.




 0
0


 May 26, 2022
May 26, 2022  By
By